Herstellung und Zusammensetzung von EPS-Sandwichpaneelen
Kernmaterialien: Verständnis von expandierbarem Polystyrol
Expandierbares Polystyrol (EPS) ist ein Schäumstoff aus Kunststoff, der aufgrund seiner Vielseitigkeit in verschiedenen Anwendungen, insbesondere im Bauwesen, in der Verpackungsindustrie und bei Isolierungen bekannt ist. EPS entsteht aus kleinen Polystyrolkügelchen, die sich beim Kontakt mit Dampfwärme bis zu 50-mal ihres ursprünglichen Volumens ausdehnen können. Dieser Ausdehnungsprozess erzeugt ein leichtes, aber stabiles Material, das für eine Vielzahl von Anwendungen geeignet ist. Bei der Herstellung EPS-Sandwichplatten , ist die Auswahl von hochwertigem EPS entscheidend, um die strukturelle Integrität und Langlebigkeit der Paneele sicherzustellen. Die Verwendung von hochwertigem EPS hilft dabei, eine gleichbleibende Qualität sowie Effektivität bei der Isolierung und Haltbarkeit aufrechtzuerhalten.
Produktionsprozess: CFC-freie Fertigungstechniken
Die Herstellung von EPS-Sandwichpaneelen umfasst eine Reihe gut abgestimmter Schritte, beginnend mit der Auswahl der Rohmaterialien und endend mit dem Veredeln der Paneele. Zunächst werden die ausgewählten EPS-Perlen durch kontrollierte Erwärmung expandiert. Dieser Schritt ist entscheidend, um die Dichte und die Isoliereigenschaften des Endprodukts zu bestimmen. Nach der Expansion werden die Perlen unter Druck zu Paneelen in der gewünschten Form und Größe geformt. Zu beachten ist, dass moderne Fertigungsverfahren für EPS-Paneele CFC-frei sind und dadurch die Umweltbelastung erheblich reduziert wird. Durch die Anwendung umweltfreundlicher Produktionsmethoden tragen Hersteller zu signifikanten Reduktionen schädlicher Emissionen bei und unterstützen nachhaltige Baupraktiken.
Material-Eigenschaften: Dichte und Isolierwert im Gleichgewicht
Bei EPS-Sandwichpaneelen beeinflusst die Dichte des Kernmaterials direkt die Isolierleistung. Paneel mit höherer Dichte bieten in der Regel eine bessere Isolierung, können jedoch höhere Materialkosten verursachen. Das richtige Gleichgewicht zwischen Dichte und Isolierwert zu finden, ist entscheidend, um Kosteneffizienz und Energieeffizienz in Gebäuden zu erreichen. Laut Branchendaten können optimierte EPS-Paneele erhebliche Energieeinsparungen ermöglichen und die Heiz- und Kühlkosten in Wohn- und Gewerbegebäuden senken. Durch die gezielte Nutzung dieser Materialeigenschaften können Bauunternehmen und Architekten energieeffiziente Lösungen entwickeln, die sowohl wirtschaftlich als auch ökologisch vorteilhaft sind.
Hauptvorteile der EPS-Kernkonstruktion
Hervorragende Wärmedämmung mit niedrigen k-Werten
EPS-Sandwichpaneele sind bekannt für ihre hervorragende Wärmedämmung, wobei K-Werte als entscheidendes Maß für ihre Effektivität dienen. K-Werte, auch Wärmeleitfähigkeitswerte genannt, zeigen, wie gut ein Material den Wärmestrom verhindert. Niedrigere K-Werte bedeuten bessere Dämmung und somit eine höhere Energieeffizienz. Die überlegenen Dämmeigenschaften von EPS können die Heiz- und Kühlkosten in Wohn- und Gewerbegebäuden erheblich reduzieren. Durch die Minimierung von Energieverlusten tragen diese Paneele zu einem behaglichen Raumklima bei und führen langfristig zu Kosteneinsparungen. Beispielsweise können gedämmte Gebäude bis zu 50 % Energie einsparen im Vergleich zu ungedämmten Strukturen, wodurch EPS-Paneele unverzichtbar für nachhaltige Bauprojekte sind.
Leichtbauweise: Unter 10 kg/m² für einfache Handhabung
Eines der herausragenden Vorteile von EPS-Sandwichpaneelen ist ihr leichte Bauweise, die in der Regel weniger als 10 kg/m² wiegt. Dieses Merkmal ermöglicht eine einfache Transport- und Handhabung sowie eine beschleunigte Installation, wodurch Bauprozesse vereinfacht und der Personalaufwand reduziert wird. Leichte Paneele tragen zudem zu ergonomischen Vorteilen bei, da sie die körperliche Belastung der Arbeiter minimieren und Projektzeiten verkürzen. Studien haben gezeigt, dass der Einsatz leichter Baustoffe wie EPS-Paneele die Arbeitskosten um bis zu 20 % senken kann. Eine solche Effizienz kommt nicht nur den Bauunternehmen zugute, indem sie die Arbeitszeit vor Ort reduziert, sondern verbessert auch das gesamte Projektmanagement und bietet eine praktische Lösung für verschiedene Bauanwendungen.
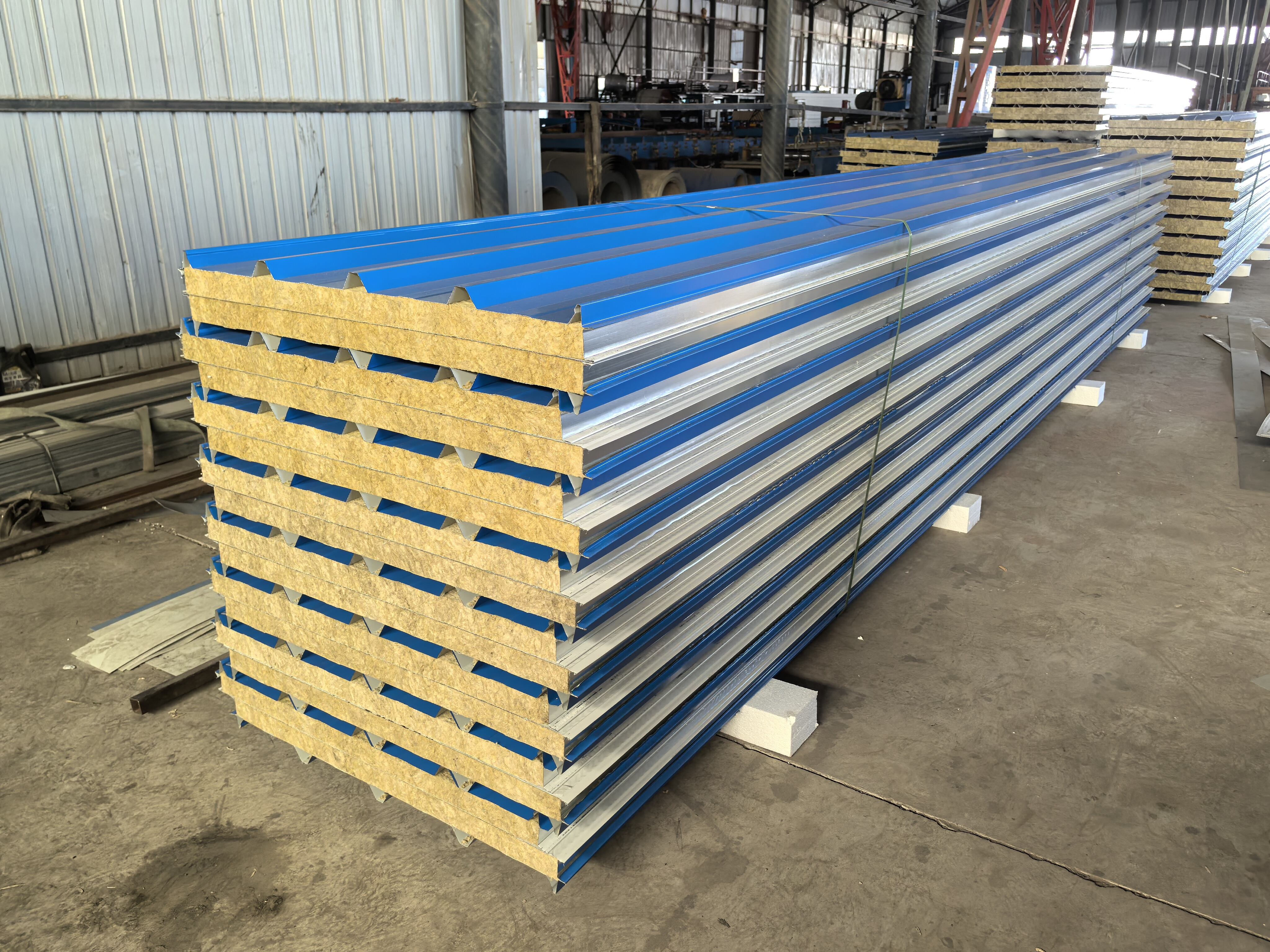
Feuchtigkeitsbeständigkeit in feuchten Umgebungen
Die geschlossenzellige Struktur von EPS spielt eine entscheidende Rolle bei der Gewährleistung von Feuchtigkeitsbeständigkeit und eignet sich somit ideal für den Einsatz in feuchten Umgebungen. Diese strukturelle Eigenschaft stellt sicher, dass EPS-Platten Wasser nicht aufnehmen, sondern ihre Integrität und Isoliereigenschaften auch in nassen Umgebungen beibehalten. Die Feuchtigkeitsbeständigkeit ist besonders wichtig für Anwendungen wie Kältespeicherung und langlebige Infrastruktur, bei denen die Aufrechterhaltung optimaler Bedingungen von zentraler Bedeutung ist. Expertenstudien bestätigen die Zuverlässigkeit von EPS in feuchtem Klima und betonen dessen Stabilität sowie die geringe Anfälligkeit für feuchtigkeitsbedingte Probleme. Folglich sind EPS-Platten hoch geschätzt für Anwendungen, die eine hohe Feuchtigkeitsbeständigkeit erfordern.
Kosteneffizienz über den gesamten Projekt-Lebenszyklus
EPS-Sandwichpaneele bieten während des gesamten Projektzyklus, von der ursprünglichen Konstruktion bis hin zur laufenden Wartung, erhebliche Kosteneffizienzvorteile. Ihre überlegene Energieeffizienz führt zu langfristigen Einsparungen und verringert die finanzielle Belastung sowohl für private Eigentümer als auch für Unternehmen. Die Kapitalrendite (ROI) ist aufgrund des reduzierten Energieverbrauchs und der erhöhten Langlebigkeit günstig, wodurch EPS-Paneele zu einer finanziell sinnvollen Wahl werden. Studien zeigen, dass die Lebenszykluskosten von Gebäuden, die mit EPS-Paneele konstruiert wurden, um 30 % niedriger sein können als bei herkömmlichen Materialien, was deren wirtschaftlichen Vorteil unterstreicht. Die Verwendung von EPS-Paneele entspricht somit den heutigen Anforderungen an effiziente und nachhaltige Baulösungen.
Industrie- und Handelsanwendungen
Kühlhäuser und Kühltransporte
EPS-Sandwichpaneele spielen eine entscheidende Rolle bei der Aufrechterhaltung konstanter Temperaturen in Kühllagern und beim gekühlten Transport. Diese Paneele gewährleisten die Erhaltung von verderblichen Waren durch hervorragende Wärmedämmung, was für die Einhaltung von gesetzlichen Vorschriften in temperaturkontrollierten Umgebungen entscheidend ist. Tatsächlich haben Studien gezeigt, dass die Verwendung von EPS in solchen Anwendungen den Energieverbrauch erheblich reduzieren kann, aufgrund der geringen Wärmeleitfähigkeit von EPS. Beispielsweise hilft EPS beim gekühlten Transport, optimale Innentemperaturen aufrechtzuerhalten, wodurch der ständige Energiebedarf zur Steuerung der Kühlsysteme verringert wird. Da EPS-Sandwichpaneele dabei helfen, Einrichtungen strengen gesetzlichen Vorgaben zu entsprechen, sind sie in der Kälte- und Lagerlogistik sowie beim gekühlten Transport unverzichtbar.
Geflügelställe und landwirtschaftliche Klimatechnik
Geflügelställe erfordern eine spezifische Klimaregelung, um optimale Bedingungen für die Gesundheit und Produktivität des Geflügels aufrechtzuerhalten, und EPS-Sandwichpaneele erfüllen diese Anforderungen effektiv. Diese Paneele bieten hervorragende Wärmedämmung und helfen dabei, Temperatur und Luftfeuchtigkeit zu regulieren, die für das Wohlergehen von Geflügel entscheidend sind. Eine Studie im Bereich der landwirtschaftlichen Anwendungen hob die Rolle von EPS bei der Verbesserung der Klimakontrolle hervor, was zu gesünderem Geflügel und einer höheren Eierproduktion führte. Ein wesentlicher Erkenntnis von Industrieexperten ist, dass eine ordnungsgemäße Dämmung mit EPS Hitzestress beim Geflügel reduziert und somit die Gesamtproduktivität steigert. Diese Vorteile machen EPS-Paneele zur bevorzugten Wahl für landwirtschaftliche Gebäude, die auf die Optimierung der Tierhaltungsbedingungen abzielen.
Temporäre Strukturen und modulare Baustellenbüros
EPS-Panele bieten mehrere Vorteile für temporäre Strukturen, wie modulare Baustellenbüros, aufgrund ihrer einfachen Montage und Demontage. Diese leichten Paneele sind unkompliziert zu installieren und eignen sich somit ideal für Baustellen und Veranstaltungsmanagement-Umgebungen, die Flexibilität erfordern. Ein aktuelles Projekt nutzte beispielsweise EPS-Panele, um eine Reihe von transportablen Büros zu erstellen, die bei Bedarf leicht verschoben und wieder zusammengesetzt werden konnten, wodurch die Vielseitigkeit der Paneele unter Beweis gestellt wurde. Zu den Vorteilen solcher modularer Konstruktionen zählen reduzierte Arbeitskosten und effizientes Flächenmanagement, wodurch EPS zur idealen Option für temporäre und schnell errichtbare Strukturen wird.
Nachhaltigkeit und Umweltwirkung
Recyclbarkeit und Beiträge zur Kreislaufwirtschaft
Die Recyclingfähigkeit ist ein entscheidender Aspekt von EPS, insbesondere hinsichtlich der Umweltverträglichlichkeit. EPS, auch expandiertes Polystyrol genannt, ist aufgrund seiner Recyclingfähigkeit bekannt und kann in verschiedenen Anwendungen wiederverwendet werden, wie z. B. zur Herstellung von neuem Polystyrol produkte , Isolierung oder sogar als Pflanzenbehälter verwendet. Diese Praktiken unterstützen die Prinzipien einer Kreislaufwirtschaft, indem sie Abfälle minimieren und die kontinuierliche Nutzung von Ressourcen fördern. Durch den Kreislauf von EPS-Materialien zurück in die Produktion können Industrien nicht nur Abfälle reduzieren, sondern auch Energie und Rohmaterialien schonen. Ein Beispiel für eine erfolgreiche Recyclinginitiative ist das Programm der EPS Industry Alliance, das großen Erfolg bei der Umwandlung von verwendetem EPS in neue Produkte erzielt hat. Somit ist die Recyclingfähigkeit von EPS ein entscheidender Faktor, um eine nachhaltige Zukunft voranzutreiben.
Erfüllen von Grünbau-Zertifizierungsstandards
EPS wird zunehmend zu einem entscheidenden Material, um grüne Gebäudezertifizierungen wie LEED zu erreichen. Dank seiner hervorragenden Isolierfähigkeit trägt EPS dazu bei, die Energieeffizienz von Gebäuden zu verbessern – ein entscheidender Faktor für solche Zertifizierungen. Dieses Material erfüllt mehrere Kriterien grüner Zertifizierungen, darunter Energieeffizienz, Ressourceneffizienz und Qualität der Innenraumumgebung. Statistiken zeigen, dass zahlreiche Gebäude mithilfe von EPS grüne Zertifizierungen erhalten haben, was auf seine Fähigkeit zurückzuführen ist, die Kohlenstoffbilanz eines Gebäudes zu reduzieren und gleichzeitig thermische Effizienz zu gewährleisten. Somit erweist sich EPS als wertvolles Material im Bereich der umweltfreundlichen Bauweise, da es strengen Umweltstandards genügt und zu einer nachhaltigeren gebauten Umwelt beiträgt.
Fortschritte bei bio-basierten EPS-Formulierungen
Neue Entwicklungen bei bio-basierten EPS-Formulierungen setzen im Baugewerbe neue Maßstäbe in Sachen Nachhaltigkeit. Forscher entwickeln Alternativen zu EPS mit geringerem Umweltimpact, um der Marktnachfrage nach umweltfreundlicheren Lösungen gerecht zu werden. Dieser Trend spiegelt umfassendere ökologische Vorteile wider, wie etwa geringere Kohlenstoffemissionen und eine reduzierte Abhängigkeit von fossilen Brennstoffen. Experten auf diesem Gebiet, wie beispielsweise bei Grand View Research, bezeichnen diese Formulierungen als wegweisend, um sowohl die Anforderungen der Industrie als auch Nachhaltigkeitsziele zu erreichen. Angesichts von Marktanalsen, die eine positive Entwicklung für diese umweltfreundlichen Alternativen prognostizieren, etabliert sich bio-basiertes EPS zunehmend als nachhaltige Lösung für zukünftige Bauvorhaben.
Vorteile bei der Installation und Wartung
Schneller Zusammenbau für Bauzeiträume
EPS-Panele sind ein Game-Changer, wenn es darum geht, die Montagezeit im Vergleich zu herkömmlichen Baustoffen zu reduzieren. Die Effizienz von EPS-Paneelen ermöglicht eine schnellere Installation und verkürzt Projektzeiträume erheblich. Beispielsweise berichten Projekte, die EPS-Panele verwenden, von bis zu 50 % weniger Bauzeit, was sich direkt auf die Projektabwicklungspläne auswirkt. Eine solch schnelle Montage beschleunigt nicht nur den Zeitplan, sondern reduziert auch Arbeitskosten und kommt Auftragnehmern und Entwicklern zugute. Aussagen von Auftragnehmern betonten, dass mit EPS-Paneelen eine schnellere Montage möglich ist, wodurch sie engste Fristen einhalten können, ohne Kompromisse bei der Qualität einzugehen.
Minimaler Wartungsaufwand
Eine der herausragenden Eigenschaften von EPS-Sandwichpaneelen ist ihr geringer Wartungsaufwand, der sich in erheblichen langfristigen Einsparungen für Immobilienbesitzer niederschlägt. EPS-Paneele sind äußerst langlebig unter verschiedenen Umweltbedingungen und bieten eine ausgezeichnete Widerstandsfähigkeit gegen Fäulnis, Schädlingsbefall und Feuchtigkeit. Diese Langlebigkeit macht sie zur bevorzugten Wahl in Regionen mit extremen Wetterbedingungen. Laut Daten sind die Wartungskosten für EPS-Paneele deutlich geringer als bei herkömmlichen Baustoffen, was die Attraktivität der Verwendung von EPS im Bauwesen weiter erhöht. EPS-Paneele gewährleisten somit nicht nur langfristig Ästhetik und strukturelle Integrität, sondern reduzieren auch die finanzielle Belastung durch Wartungskosten.
Nachrüstung bestehender Strukturen
EPS-Panele sind nicht nur auf Neubauten beschränkt; sie sind auch bei der Nachrüstung bestehender Gebäude äußerst effektiv, verbessern die Isolierung und senken die Energiekosten. Durch die Integration von EPS-Panels können ältere Gebäude moderne Energieeffizienzstandards erreichen und somit Heiz- und Kühlkosten reduzieren. Dieser Prozess ist häufig mit behördlichen Anreizen für energieeffiziente Modernisierungen vereinbar, wodurch der Übergang wirtschaftlich vorteilhaft wird. Erfolgsgeschichten von Nachrüstungsprojekten haben deutliche Verbesserungen bei der Wärmedämmung und Energieeffizienz durch EPS-Integration gezeigt. Solche Projekte unterstreichen die Praktikabilität und Kosteneffizienz von EPS-Panels bei der Modernisierung bestehender Gebäude, um aktuellen Standards gerecht zu werden.
Neue Trends in der EPS-Panel-Technologie
Flammhemmende Additive für erhöhte Sicherheit
Der zunehmende Bedarf an feuerbeständigen Baustoffen hat zu Fortschritten in der EPS-Technologie geführt, insbesondere durch die Zugabe von Flammschutzmitteln. Diese Zusatzstoffe sind entscheidend, um die Entflammbarkeit von EPS-Produkten zu reduzieren und somit die Sicherheit zu erhöhen. Die Einhaltung internationaler Brandschutzstandards, wie sie von ASTM und EN festgelegt wurden, ist von großer Bedeutung, um sicherzustellen, dass EPS-Platten die strengen Anforderungen für den Bau verwenden erfüllen. Als Beleg für ihre Wirksamkeit berichten viele Gebäude, die mit verbessertem EPS errichtet wurden, von weniger Brandereignissen, was die schützenden Eigenschaften der Zusatzstoffe verdeutlicht. Diese Fortschritte sorgen nicht nur für mehr Sicherheit, sondern tragen auch dazu bei, EPS in einer Vielzahl von Bauprojekten stärker einzusetzen.
Prognosen zum Wachstum regionaler Märkte
Der Markt für EPS-Sandwichpaneele erlebt ein starkes Wachstum, insbesondere in Regionen wie Asien-Pazifik und Nordamerika. Laut jüngsten Marktforschungen wird prognostiziert, dass der globale Markt von 2024 bis 2030 mit einer durchschnittlichen jährlichen Wachstumsrate (CAGR) von 7,7 % expandieren wird. Dieses Wachstum wird durch eine zunehmende Nachfrage nach energieeffizienten Baulösungen vorangetrieben, unterstützt durch staatliche Politiken, die nachhaltige Baustoffe fördern. Zudem tragen die steigende urbane Bevölkerung und erhöhte Investitionen in Infrastruktur zu diesen positiven Trends bei. Da das Bewusstsein für Energieeinsparung und ökologische Nachhaltigkeit wächst, steigt auch die Nachfrage nach EPS-Paneele, wodurch sie zu einem entscheidenden Akteur in der Zukunft der Bauindustrie werden.
Smart Panel Integration mit IoT-Systemen
Mit dem Aufkommen von Smart-Building-Technologien entwickeln sich EPS-Panele weiter, um IoT-Systeme zu integrieren, und bieten neue Funktionen, die Energiemanagement und Automatisierung verbessern. Diese intelligenten Panele spielen eine entscheidende Rolle bei der Optimierung von Gebäudeoperationen, indem sie eine Echtzeitüberwachung und Steuerung der Umweltbedingungen ermöglichen. Studien haben gezeigt, dass der Einsatz von Smart-Technologien zu erheblichen Reduzierungen der Betriebskosten führen kann und somit wirtschaftliche wie auch ökologische Vorteile bietet. Durch die Kombination der Vorteile von EPS-Paneelen mit IoT-Funktionen lässt sich eine gesteigerte Effizienz erreichen, wodurch Bauprojekte nachhaltiger und kosteneffizienter werden. Die Integration dieser Technologien markiert einen wegweisenden Schritt in der Entwicklung von Baustoffen und trägt den modernen Anforderungen nach intelligenterer Infrastruktur Rechnung.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wofür werden häufig EPS-Sandwichpanele verwendet?
EPS-Sandwichpaneele werden häufig für Isolationszwecke im Bauwesen verwendet, beispielsweise in Kühllagerräumen, Modulbüros und Geflügelställen. Sie bieten eine hervorragende Wärmedämmung, ein leichtes Design und sind feuchtigkeitsbeständig.
Wie wirkt sich die Dichte von EPS auf die Isolationswirkung aus?
Die Dichte von EPS beeinflusst seine Isolationswirkung, wobei Paneele mit höherer Dichte in der Regel eine bessere Isolierung bieten. Dies kann jedoch auch die Materialkosten erhöhen. Eine Balance zwischen Dichte und Isolationswert ist entscheidend für kosteneffiziente Baulösungen.
Sind EPS-Paneele umweltfreundlich?
Ja, EPS-Paneele gelten aufgrund ihrer Recyclingfähigkeit und ihres Beitrags zu energieeffizienten Gebäudedesigns als umweltfreundlich. Zudem unterstützen sie nachhaltige Praktiken durch CFC-freie Herstellungsverfahren.
Können EPS-Paneele in feuchten Umgebungen verwendet werden?
Ja, EPS-Platten sind aufgrund ihrer geschlossenzelligen Struktur für feuchte Umgebungen geeignet, da diese exzellente Feuchtigkeitsbeständigkeit bietet und Wasseraufnahme verhindert.
Welche Entwicklungen gab es bei der EPS-Plattentechnologie?
Entwicklungen bei der EPS-Plattentechnologie umfassen die Zugabe von feuerhemmenden Additiven für erhöhte Sicherheit, bio-basierte EPS-Formulierungen für Nachhaltigkeit und die Integration mit IoT-Systemen für intelligente Funktionen in Gebäuden.

 EN
EN







































